MCP Server for Langfuse Prompts
The Langfuse Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server enables AI assistants and agents to interact with your Prompt Management system. The server is built directly into Langfuse at /api/public/mcp (streamableHttp), no external setup or build steps required.
Available Tools
The Langfuse MCP Server provides five tools for comprehensive prompt management in Claude Code and other MCP clients:
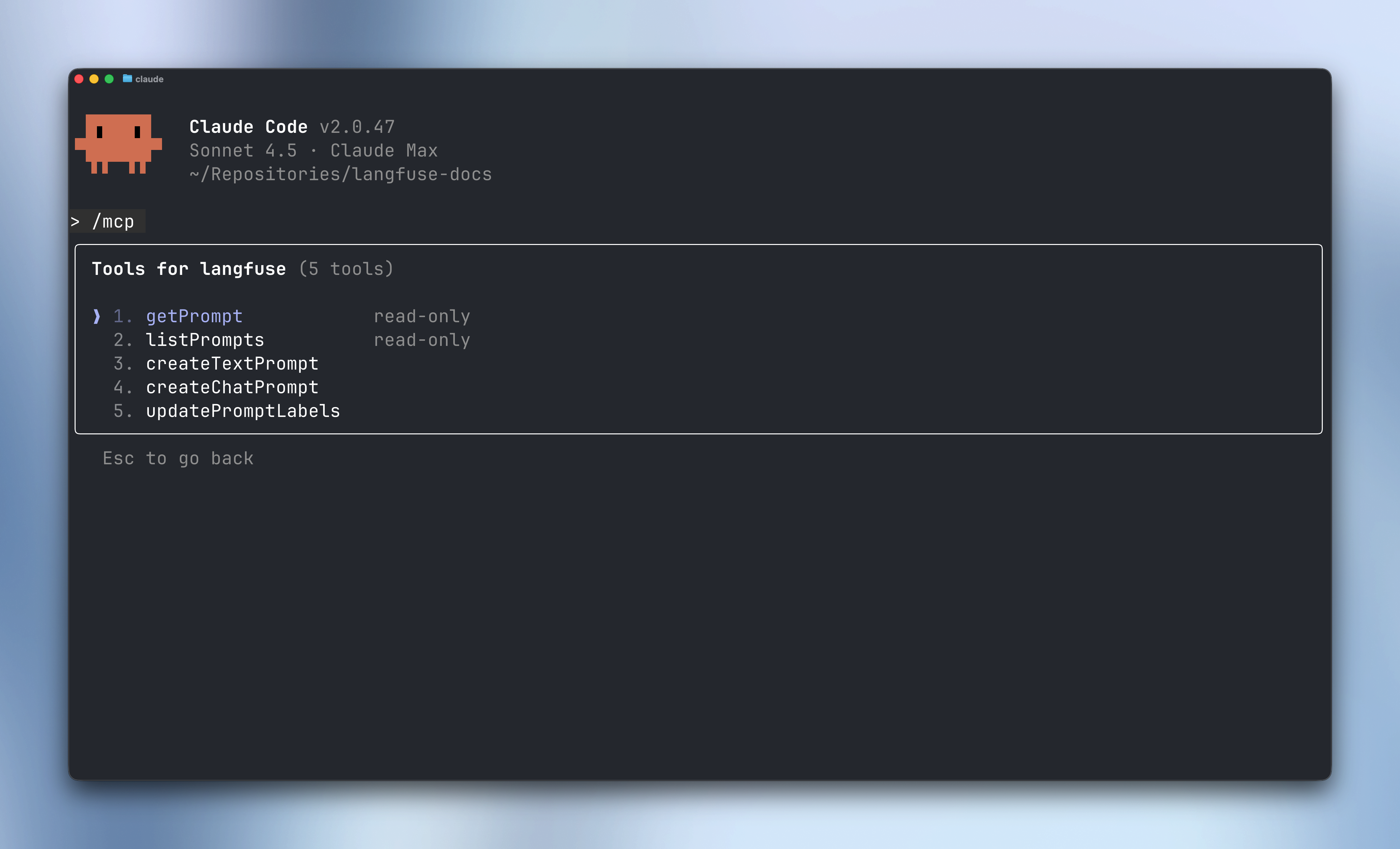
Features
Read Operations
-
getPrompt- Fetch a specific prompt by name- Optional
labelparameter (e.g., “production”, “staging”) - defaults to “production” - Optional
versionparameter to get a specific version number - Returns compiled prompt with metadata and configuration
- Optional
-
listPrompts- Browse all prompts in your project- Optional filtering by
name,tag, orlabel - Cursor-based pagination for large prompt libraries
- Returns prompt metadata including available versions and labels
- Optional filtering by
Write Operations
-
createTextPrompt- Create a new text prompt version- Simple string content with
{{variable}}template syntax - Optional labels (e.g.,
["production", "staging"]) - Optional config object for model settings
- Optional tags for organization
- Optional commit message to document changes
- Automatically increments version number
- Simple string content with
-
createChatPrompt- Create a new chat prompt version- OpenAI-style message format with role and content
- Supports system, user, and assistant message roles
- Template variables work in message content
- Same label, config, tag, and commit message options as text prompts
-
updatePromptLabels- Manage labels across prompt versions- Move labels between versions (e.g., promote staging to production)
- Labels are unique—setting a label on one version removes it from others
- Cannot modify the auto-managed
latestlabel - Useful for deployment workflows and version control
Setup
See the MCP Server setup guide for complete instructions on authentication and client configuration.
Example Workflows
Create a New Prompt
Ask your AI agent:
“Create a new text prompt called ‘customer-email’ with a friendly greeting template that includes name and product variables. Tag it as ‘draft’ and add a production label.”
The agent will use createTextPrompt to create the prompt version.
Promote a Prompt to Production
“Move the production label from version 2 to version 3 of the customer-email prompt”
The agent will use updatePromptLabels to update the label assignment.
Iterate on a Chat Prompt
“Create a new version of the code-review prompt with improved system instructions and add an example assistant message showing the review format”
The agent will use createChatPrompt to create a new version with enhanced content after having fetched the prompt with getPrompt.
Move Hardcoded Prompts to Langfuse
Use your AI coding agent (Cursor, Claude Code, etc.) to automatically identify hardcoded prompts in your codebase and migrate them to Langfuse Prompt Management. This workflow:
- Discovers all hardcoded prompts, system instructions, and templates in your code
- Creates the prompts in Langfuse using the MCP server
- Updates your code to fetch prompts from Langfuse at runtime
Prerequisites
Configure the Langfuse MCP Server
Follow the setup instructions to connect your AI editor to the Langfuse MCP server with your project API keys.
Run the Migration Agent
Copy and execute the following prompt in your editor’s agent mode (e.g., Cursor Agent, Claude Code):
View prompt
# Langfuse Prompt Management Migration
## Goal
Your goal is to identify hardcoded prompts in this codebase and migrate them to Langfuse Prompt Management, then update the code to fetch prompts from Langfuse at runtime.
## Rules
Before you begin, understand these fundamental rules:
1. **Preserve Business Logic**: Do not change application behavior. The only changes should be moving prompts to Langfuse and updating how prompts are retrieved.
2. **Follow the Workflow**: Execute the steps below in sequence.
3. **Use Available Tools**: Use the Langfuse MCP server tools (`listPrompts`, `getPrompt`, `createTextPrompt`, `createChatPrompt`, `updatePromptLabels`) to interact with Langfuse Prompt Management.
## Migration Workflow
### Step 1: Discover Hardcoded Prompts
Analyze the codebase to find all hardcoded prompts. Look for:
- System prompts or instructions passed to LLM calls
- Template strings used for prompt construction
- Multi-line strings containing AI instructions
- Variables named `prompt`, `system_prompt`, `instructions`, `template`, etc.
- Files in directories like `prompts/`, `templates/`, or similar
Present a list of all discovered prompts with:
- File path and line numbers
- The prompt content (truncated if very long)
- Suggested prompt name for Langfuse (e.g., `customer-support-agent`, `code-review-assistant`)
- Prompt type: text or chat (OpenAI message format)
Ask me to confirm which prompts to migrate before proceeding.
### Step 2: Check Existing Prompts in Langfuse
Use the `listPrompts` tool to check what prompts already exist in the Langfuse project. Compare with the prompts identified in Step 1 to avoid duplicates.
### Step 3: Create Prompts in Langfuse
For each confirmed prompt, create it in Langfuse:
**For simple text prompts** (single string templates):
- Use `createTextPrompt` tool
- Extract template variables and use `{{variable}}` syntax
- Add appropriate tags (e.g., `migrated`, `v1`)
- Set the `production` label for immediate use
**For chat prompts** (system/user/assistant message format):
- Use `createChatPrompt` tool
- Structure as OpenAI-style messages with roles
- Include all message types (system, user examples, etc.)
- Add appropriate tags and labels
Include a commit message describing the migration (e.g., "Migrated from codebase: path/to/file.py")
### Step 4: Propose Code Changes
Present a plan to update the codebase to fetch prompts from Langfuse at runtime. The plan should include:
1. **SDK Installation**: The Langfuse SDK package to install
2. **Environment Variables**: Required configuration (LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY, LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY, LANGFUSE_HOST if self-hosted)
3. **Code Changes**: For each migrated prompt, show the before/after code
Wait for my approval before implementing changes.
### Step 5: Implement Code Changes
After approval, make the following changes:
1. Install the Langfuse SDK using the package manager
2. Add prompt fetching code that:
- Initializes the Langfuse client
- Fetches prompts by name (optionally with label for staging/production)
- Compiles prompts with any required variables
- Handles caching appropriately for your use case
**Python example pattern:**
```python
from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()
# Fetch and compile prompt
prompt = langfuse.get_prompt("prompt-name")
compiled = prompt.compile(variable="value")
```
**JavaScript/TypeScript example pattern:**
```typescript
import { Langfuse } from "langfuse";
const langfuse = new Langfuse();
// Fetch and compile prompt
const prompt = await langfuse.getPrompt("prompt-name");
const compiled = prompt.compile({ variable: "value" });
```
3. Remove or comment out the old hardcoded prompts
4. Add documentation comments explaining the Langfuse prompt source
### Step 6: Verify Migration
After implementing changes:
1. Confirm all prompts are created in Langfuse using `listPrompts`
2. Verify prompt content is correct using `getPrompt`
3. Ask me to test the application and confirm prompts are being fetched correctly
### Step 7: Optional Enhancements
Suggest additional improvements:
- **Labels**: Set up staging/production labels for A/B testing
- **Versioning**: Explain how to iterate on prompts via Langfuse UI
- **Caching**: Configure appropriate cache TTL for your use case
- **Fallbacks**: Add fallback behavior if Langfuse is unreachable
Why Migrate Prompts?
Moving prompts from code to Langfuse Prompt Management provides several benefits:
- Iterate without deployments: Update prompts in the Langfuse UI without code changes
- Version control: Track prompt history with automatic versioning and commit messages
- A/B testing: Use labels to test different prompt versions (staging vs production)
- Collaboration: Non-technical team members can view and suggest prompt improvements
- Analytics: Link prompts to traces to measure performance across versions
Feedback
Share your experience with the Langfuse MCP server in our GitHub Discussion. We’d love to hear your feedback and use cases.
Learn More
- MCP Server Overview - Complete MCP server documentation
- Prompt Management - Learn about Langfuse prompt features
- Model Context Protocol - Official MCP documentation